Company News | 2023-12-22
The working principle of gas ballast valve
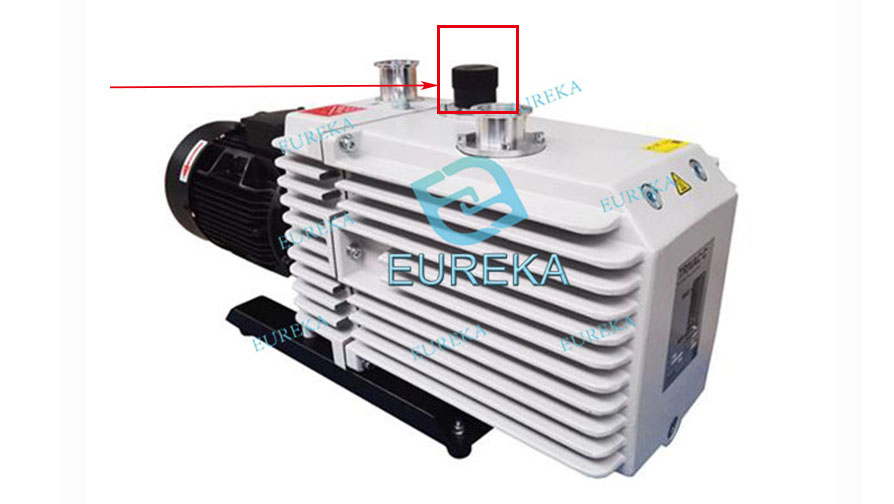

There is usually a small hole in the compression chamber of an oil-sealed rotary vane mechanical vacuum pump, and a regulating
valve is installed. When the valve is opened and the air intake is adjusted, the vacuum pump rotor rotates to a certain position. Air is
incorporated into the compression chamber through this hole to reduce the compression ratio, so that most of the vapor does not condense
and is expelled from the pump together with the incorporated gas. The valve that plays this role is called a gas ballast valve.
The gas ballast valve can accelerate the extraction of steam without contaminating the oil quality.
If the vacuum pump only pumps out permanent gas, and the gas does not liquefy due to the increase in pressure, it is what we
often call the deterioration of the pump oil. However, if a vacuum pump is used to extract humid air, there will be not only permanent
gas but also water vapor in the gas. If a pump without gas ballast is used to extract this part of the water vapor, the water vapor will
liquefy in the vacuum pump and phase with the vacuum pump oil. Melts, thereby deteriorating the vacuum pump oil, thereby reducing
the pumping speed and vacuum degree.
Analysis of water vapor in vacuum pumps
The water vapor extracted by the pump is compressed in the compression chamber until the exhaust valve opens. When the
temperature inside the pump is 60°C, the saturated vapor pressure of water at this temperature is 20kPa. Once the water vapor
in the compression process reaches At a pressure of 20kPa, water vapor begins to condense into water, but the exhaust valve
cannot be pushed open at 20kPa, because the exhaust valve is open to the atmosphere and is pressed by the exhaust valve spring,
which means that the internal pressure of the pump chamber must The exhaust valve cannot be pushed open until it is compressed
to more than 120kPa. After the water vapor is compressed, by the end of the compression, it has completely condensed into water
and mixed into the oil.
How to restore the ultimate pressure of a vacuum pump contaminated by liquefaction of condensable gas
Another use of the gas ballast valve can be to restore the ultimate pressure of the vacuum pump. Sometimes, although we use it
to extract ordinary air, it contains less condensable gas. Generally, the gas ballast valve is closed. Over time, the oil quality is gradually
contaminated by a small amount of condensable gas contained in the air. For pumps without gas ballast mechanism, the original
ultimate pressure of the pump can be restored only by replacing new oil or heating the pump oil to allow the liquefied condensable gas
to evaporate. For gas ballast pumps, as long as l is turned on The ultimate pressure of the vacuum pump can be restored in ~2h.
When the internal pressure of the gas ballast valve is lower than the external pressure, the gas ballast valve opens and the gas enters
the pump chamber so that the partial pressure of the condensable gas inside the pump chamber reaches the saturated vapor pressure at the pump temperature. The pressure of the compressed gas has reached the exhaust pressure. , discharge the condensable gas; when the internal pressure of the gas ballast valve is higher than the external pressure, the gas ballast valve closes.